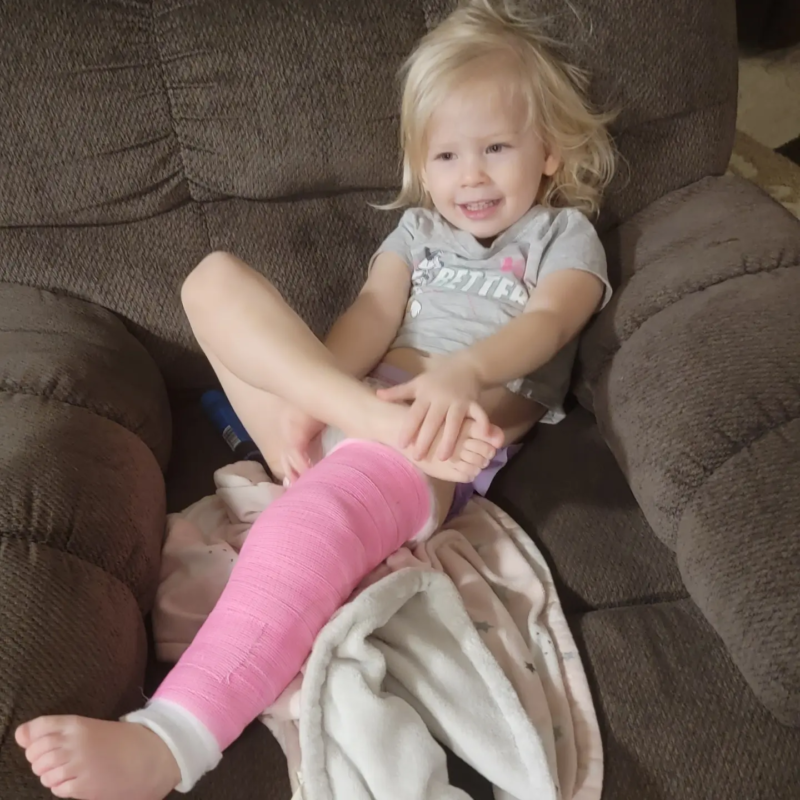
Causes of Sudden Limping in Toddlers
Why is my toddler suddenly limping without pain? It can be unsettling to notice your toddler suddenly limping without expressing pain. Understanding the potential causes is crucial for proper care and intervention. Each cause demands its own attention and approach.

Viral Infections
Viral infections can lead to muscle soreness or joint swelling, causing a toddler to limp. Often, these infections are not associated with significant pain, making it less obvious to caregivers. Breathlessness or a slight fever may accompany the limp. Keeping a close eye on additional symptoms is important for identifying viral causes.
Toddler’s Fracture
A subtle hairline break, often in the tibia, can result in a painless limp, known as a toddler’s fracture. These fractures may not always swell or bruise, making them difficult to spot. Slight discomfort and a preference for not using the affected limb could be the only signs.
Hip Disorders
Various hip disorders, including transient synovitis or hip dysplasia, can manifest as limping. They might not cause immediate pain, but could lead to longer-term issues if left unaddressed. A toddler’s reluctance to move or change in gait should prompt an evaluation for hip abnormalities.
Diagnosis of Painless Limping
When your toddler starts limping without showing any signs of pain, it’s essential to understand when to seek a pediatrician’s assistance and what diagnostic tests may be necessary. Identifying the underlying cause is critical for effective management and ensuring your child’s health and well-being.
When to See a Pediatrician
If you’re wondering ‘why is my toddler suddenly limping without pain’, it’s advisable to observe your child closely. Should the limp persist for more than a day, interfere with normal play, or if your toddler seems unwell, it is time to see a pediatrician. Any accompanying symptoms, such as fever, swelling, or redness, also warrant immediate medical attention. Early evaluation can prevent potential complications and help in prompt treatment.
Common Diagnostic Tests
To diagnose the cause behind a toddler’s limp, pediatricians often recommend a series of tests. These may include:
- X-rays: To detect fractures or bone abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: To look for signs of infection or inflammation.
- Ultrasound: Useful for examining soft tissue and hip joints.
- MRI: Provides detailed images of bones and soft tissues, helpful if initial tests are inconclusive.
Through these tests, doctors aim to rule out serious conditions and establish a diagnosis. With the results, they can develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to your toddler’s specific condition.
Management and Treatment Options
Once a diagnosis is made for why a toddler is suddenly limping without pain, a proper management plan can be laid out. Treatment varies based on the underlying causes identified during the diagnostic process.
Home Care Strategies
If the limping is a result of a mild injury or a viral infection, it can often be managed at home. Rest is essential; encourage your child to avoid putting weight on the affected leg. Ice applied to any swollen areas can reduce inflammation. Over-the-counter pain relievers may be considered if your toddler is old enough and in discomfort, though pain isn’t present initially. Always follow a pediatrician’s guidance on medication for children.
For minor limps, limiting vigorous activity and providing a supportive shoe can help. Monitor your child’s symptoms and if they worsen or do not improve, seek further medical advice. Keeping the child hydrated, especially during viral infections, and ensuring a comfortable resting area are also key.
Medical Interventions
For more serious cases, such as fractures or hip disorders, professional medical treatment is necessary. A toddler’s fracture may require a cast or splint to ensure proper healing. Hip disorders, depending on the type, could need physical therapy, or even surgery, to correct the problem.
Transient synovitis usually resolves itself, but pediatricians may recommend anti-inflammatory medications to ease symptoms. If an infection is the cause, antibiotics might be prescribed. Follow your pediatrician’s care plan closely to ensure the best outcome for your child’s health.
Overview of Transient Synovitis
Transient synovitis is a common cause of sudden limping in toddlers without pain. It is a temporary inflammation of the synovium, which is the lining of the inner joint capsule of the hip. This condition is typically self-limiting, meaning it resolves on its own with time. Nonetheless, knowing the signs and proper care approaches are crucial for parents and caregivers.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The primary symptom of transient synovitis is a sudden, painless limp. The child may also show reduced movement in the affected hip and could seem less active than usual. Diagnosis often begins with a history and physical exam by a pediatrician. If transient synovitis is suspected, the pediatrician may order tests such as an ultrasound of the hip or blood tests to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
Treatment Approaches
Most cases of transient synovitis improve without intensive medical treatment. The mainstay of treatment is rest and monitoring. A pediatrician may recommend over-the-counter anti-inflammatories to reduce any potential discomfort. Persistent symptoms or concerns should be revisited with a healthcare professional, although the condition typically clears up within a week to ten days. It is important to follow through with the pediatrician’s advice to ensure complete recovery. Parents should ensure their child avoids strenuous activities until they fully recover, and regular follow-ups may be advised to confirm that the child’s hip is healing properly.
Role of Hip Dysplasia
Hip dysplasia is a significant cause of sudden, painless limping in toddlers. It involves the improper development of the hip joint, where the ball and socket do not fit snugly. This misalignment can cause a toddler to limp, often without experiencing pain. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in managing this condition effectively and preventing long-term complications.
Identifying Hip Dysplasia in Toddlers
Identifying hip dysplasia early can be challenging as toddlers may not show clear signs of discomfort. Parents and caregivers should look for signs such as uneven leg lengths, a limp, or difficulty walking. A toddler favoring one side or showing a waddling gait when walking can also be indicators. These signs warrant a consultation with a pediatrician to explore the possibility of hip dysplasia.
Long-term Management
Long-term management of hip dysplasia aims to realign the hip joint and promote normal hip function. Treatment options vary depending on the severity and may include harnesses, braces, or surgery. Physical therapy is often recommended to strengthen the hip and surrounding muscles. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed. Early and consistent treatment is key to preventing future hip problems and ensuring a healthy development.
Preventive Measures for Limping
Preventing limping in toddlers starts with understanding and implementing certain precautions. Parents and caregivers can take proactive steps to ensure their child’s well-being and minimize the risk of limping without pain. Here are some crucial preventive measures to consider.
Importance of Proper Footwear
Choosing the right footwear is vital for your child‘s foot health and overall mobility. Footwear that fits well and provides proper support can prevent many cases of limping. Look for shoes with a good grip, adequate cushioning, and flexibility. This contributes to a stable and balanced walk. Avoid shoes that are too tight or too loose, as they can lead to poor walking patterns and potentially cause limping. Regularly check your child’s shoe size, especially during growth spurts, to ensure they are wearing the right size.

Regular Pediatric Check-ups
Routine check-ups with a pediatrician are essential to monitor your child’s developmental milestones and address any concerns early. During these visits, a pediatrician can spot signs of conditions like hip dysplasia or subtle limb abnormalities that might cause limping. Regular screenings help in early detection of potential issues, allowing for timely intervention and management. Encourage these visits even if no symptoms are noticed, as some conditions leading to limping may not initially display obvious signs.